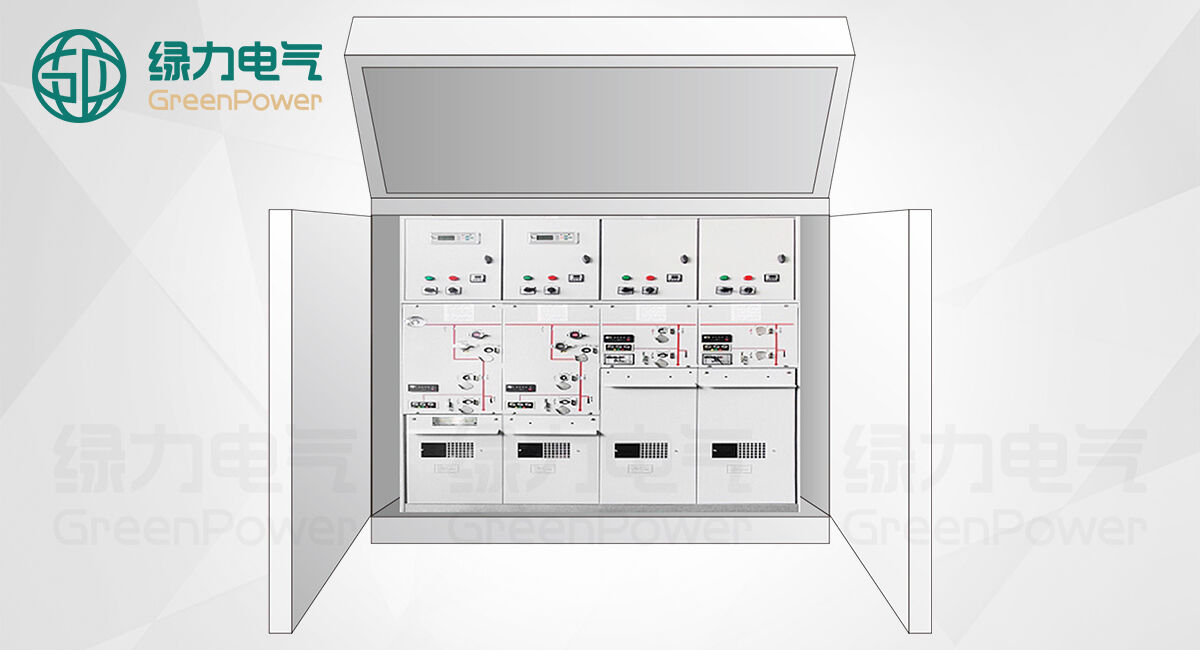
The Ring Main Unit, commonly known as RMU, serves as a compact switchgear system enclosed in metal housing. These units manage, safeguard, and separate medium voltage distribution networks that usually run between 10kV and 35kV levels. Inside these enclosures we find several key components working together: vacuum circuit breakers stop faults from spreading, disconnectors allow technicians to work safely on equipment, current limiting fuses protect against excessive currents, and all connected cables remain properly insulated within the unit itself. What makes this setup so valuable is how it takes up minimal space yet keeps workers safe during operations. That's why many cities install them in tight spots like downtown substations, factories needing reliable power supply, or connection points for wind farms and solar installations. Plus, since they support both radial and ring network layouts, operators get the freedom to quickly contain problems and redirect electricity flow when needed, which matters a lot in maintaining consistent service delivery.
Ring Main Units act as smart connection points within medium voltage looped networks, using two separate power sources to build in backup capabilities. When operating at common distribution levels around 11kV or 33kV, these units spot problems such as broken cables or malfunctioning transformers typically within 100 to 300 milliseconds. What makes them really effective is their ability to cut off just the faulty section without disrupting the whole system. The rest of the network takes over by finding alternative routes for electricity delivery, so service stays online even during issues. This kind of N minus one redundancy turns regular electrical grids into something resembling self healing systems. For places where continuous operation matters most – think hospitals needing life support equipment, data centers running critical applications, or factories producing goods that require constant monitoring – losing power isn't just inconvenient. According to research from the Ponemon Institute published in 2023 about data center outages, businesses can lose upwards of seven hundred forty thousand dollars every single hour when operations come to a halt.
Modern RMUs equipped with microprocessor based protection relays can spot short circuits and earth faults almost instantly, usually within a few milliseconds. These smart systems then cut off just the problematic part of the network while keeping everything else running normally. Take a damaged cable for instance it gets isolated in less than half a second, and power comes back automatically through another path in the ring network. Traditional radial setups just cant match this kind of performance. According to some recent studies from Grid Reliability folks, this approach cuts down on power outages by around 80%. What makes these systems so effective is their ability to tell the difference between temporary glitches that clear themselves up and real problems that need attention. When something clears on its own, the system will try reconnecting automatically. But if there's still an issue, it locks out that section and sends alerts remotely. This means quicker fixes, less wear and tear on equipment, and fewer headaches for people working in both industrial areas and city grids where uninterrupted service matters most.
RMUs offer several layers of protection for both infrastructure and personnel working around them. The vacuum circuit breakers can stop fault currents within just three cycles, which helps protect transformers and underground cables from excessive heat damage. Inside these units are gas insulated sections, usually filled with SF6 or clean air technology. These compartments trap arc energy effectively, cutting down on dangerous exposure levels for maintenance workers by about 60 percent when compared to older air insulated systems according to IEEE standards from 2023. When it comes to ground faults, detection systems kick in early enough to catch earth leakage problems before they start wearing down insulation materials. Plus there are those mechanical and electrical locks that stop accidental contact with live components. And let's not forget remote operations too. Being able to switch things on and off from afar means fewer trips into hazardous areas, making everything safer overall without slowing down response times much at all.
Modern RMUs now come equipped with IoT sensors and standard communication protocols like IEC 61850 and DNP3 that allow real time telemetry. These systems transmit important data such as load current readings, temperature measurements, signs of partial discharge, and overall equipment status straight to SCADA systems and other grid management software. Take thermal monitoring for example. According to Grid Operations Journal from last year, it spots unusual conductor heating problems about 68 percent quicker compared to those old school thermographic surveys done manually. This early detection makes it possible to balance loads proactively and prevent overloads before they happen. When SCADA systems are properly integrated, operators can perform secure remote switching operations. This means no one needs to physically go out to the site for regular system adjustments or when emergencies require equipment isolation. As a result, average power outages in cities get resolved around 40% faster than before these technologies were implemented.
RMUs equipped with IoT technology collect detailed operational information that makes predictive maintenance possible. When we look at things like vibrations, temperature changes, and partial discharges, these measurements can actually spot problems developing in components such as breakers, bushings, and insulators long before they fail completely. Some utilities reported back in 2023 that their maintenance schedules based on algorithms helped extend the lifespan of RMUs by around seven years on average. What's really interesting is how this data also supports digital twin technology. These virtual models let engineers see how the power grid might react to different situations. For instance, when solar power suddenly increases or loads shift unexpectedly, operators can test their response plans first in the virtual world. This approach helps them fine tune protective systems and manage about 35% more renewable energy sources without risking grid instability.
Ring Main Units get placed where they're needed most to handle different reliability issues, space constraints, and day-to-day operations throughout today's electrical networks. Cities benefit greatly from them because their small size and modular setup makes upgrading substations much faster in crowded downtown areas. Installation times drop around 30% compared to traditional methods, which means fewer outages for people living in densely populated regions. Industrial facilities rely on RMUs too when switching between regular grid power and backup sources like diesel generators or battery storage systems. This helps keep manufacturing running smoothly without unexpected shutdowns that cost money. When it comes to renewable energy projects such as solar farms connecting to the main grid or wind powered microgrids, RMUs play a crucial role managing power flowing both ways, keeping voltages stable even when weather conditions change, and allowing parts of the grid to operate independently if necessary. All told, these units make the overall power system more robust, cut down on long term maintenance expenses somewhere around 15%, and help bring existing infrastructure into line with newer smart grid requirements. That's why many experts see RMUs as essential building blocks for creating flexible, environmentally friendly electricity distribution networks.
 Hot News
Hot News2026-02-16
2026-02-14
2026-02-12
2026-02-09
2026-02-06
2026-02-02